Difference between revisions of "Reference Table"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{:Data Description References}} | |||
{ | |||
== Usage Information == | == Usage Information == | ||
d_references is the dictionary for all encoded data. | d_references is the dictionary for all encoded data. | ||
=== SQL === | === SQL === | ||
| Line 42: | Line 11: | ||
Example: | Example: | ||
SELECT Sex, | SELECT Sex,sRef.ReferenceValue as SexCaption FROM `cases` LEFT JOIN d_references as sRef ON SexRef.ReferenceGlobalID = cases.Sex; | ||
For more examples read the [[SQL Examples]] section | |||
=== RooDataServer === | === RooDataServer === | ||
| Line 48: | Line 19: | ||
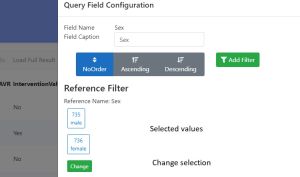
All fields using references provide simple filters to select references. | All fields using references provide simple filters to select references. | ||
On export RooDataServer will per default export the text value of an encoding. | On export RooDataServer will per default export the text value of an encoding. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:43, 3 November 2022
The d_references table contains information on all encoded data fields of the SICdb dataset. Each field, that has "Reference" as field type, is associated with the ReferenceGlobalID in the d_references table. Additionally ReferenceUnit describes the unit of measurement used for this field. Refer to chapter SQL Examples to learn how to easily use this table in relational databases.
| Name | Type | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| ReferenceGlobalID | Integer | The unique ID for the reference | Use this identifier as dictionary for alle encoded fields |
| ReferenceValue | Text | Reference value | i.e. "Creatinine" |
| ReferenceName | Text | The name of the reference | i.e. "Laboratory" |
| ReferenceUnit | Text | The unit of this item if applicable | i.e. "mg/dl" |
Usage Information
d_references is the dictionary for all encoded data.
SQL
Use a join query to get the reference value.
Example:
SELECT Sex,sRef.ReferenceValue as SexCaption FROM `cases` LEFT JOIN d_references as sRef ON SexRef.ReferenceGlobalID = cases.Sex;
For more examples read the SQL Examples section
RooDataServer
All fields using references provide simple filters to select references. On export RooDataServer will per default export the text value of an encoding.
Note
To reduce the amount of tables there is no table describing references as there is no significant gain of information expected. This may change in later versions of dataset. To enumerate a reference use table d_references.ReferenceName, which is an immutable, case sensitive key to a reference.